Vitamin D Fact Sheet
Understanding this Vitamin D fact sheet, I am sure you will agree that sensible exposure to the sun's UVB rays and the resultant Vit D3 boost, should be seen as essential to good health today. The 'sunshine vitamin' is named thus because it is produced primarily in the skin through a chemical reaction that requires UVB sunlight rays. I like to believe that it is also because for thousands of years it used to be an effective treatment for a number of diseases.
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 1 - What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is one of the chemicals produced by the skin that is ultimately found in cells throughout the body and is essential to the health of our bones and muscles. It helps the body to absorb calcium without which you may develop soft, thin and brittle bones, a condition known as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
Vitamin D is important to the body in many other ways as well. Muscles need it to move, for example, nerves need it to carry messages between the brain and every body part, and the immune system needs vitamin D to fight off invading bacteria and viruses.
Vitamin D is a precursor to a hormone, otherwise known as a prohormone. It is also fat-soluble and comes in 2 major forms - Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3. Vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol, is acquired through eating some foods like mushrooms whilst Vitamin D3, or ergocalciferol, is acquired through an interaction between UVB radiation and our skin. Both can be acquired through supplementation but Vitamin D3 is considered superior from a human health benefit perspective.
From an overall health perspective, Vitamin D plays an important role in the general maintenance of our organ systems, efficient mineral absorption, bone health and general immune well being. Vitamin D enhances the efficiencies of calcium and phosphorus absorption in the intestines and calcium in the kidneys which results in effective regulation of these minerals in one's blood.
Where bones are concerned, Vitamin D is essential for the strong development of bone formation but if too high can actually promote some resorption of bone and counteract this strength.
As an immunosuppressant it is quite powerful in that is a major mechanism to remove pathogens, bacteria and dead tissue cells. It also promotes anti-tumor activities.
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 2 - Sensible skin exposure
Research undertaken by Edward D. Gorham, William B.Grant, et al on the geographic distribution of Ultraviolet A (UVA) and B (UVB) was done in order to understand the importance from a biological perspective. There was considerable variation in UVB (Figure 1) and UVA (Figure 2) irradiance among countries. Both types of ultraviolet radiation predominated in areas near the equator and were markedly lower in areas distant from it.
UVB is needed for photosynthesis of vitamin D3. Since this is the best source of Vitamin D3 and we get this by exposing our skin to the sun's UVB rays, there are some important considerations in managing our exposure to the sun.
The sun's UVB radiation strength will vary according to:
- Season. At the height of summer, the UVB rays are more direct for longer times during the day and therefore more likely to create good Vitamin D levels.
- Latitude. The higher the latitude the lower the strength of the sun's UVB rays. see map below.
- Altitude. People living at higher altitudes generally have higher Vitamin D levels. UVB radiation intensity increases with altitude by about 15% per 1000 m because of decreasing ozone. Moreover, the photoconversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3 has been shown to increase with altitude, particularly above 2000 m.
- Cloud cover and pollution. The more cloud cover or pollution in the atmosphere the less UVB can penetrate. eg. Variations in anthropogenic sulfate aerosols reveals low density in most of sub-Saharan Africa but high levels in China. Also, low cloud cover in sub-Saharan Africa vs high cover in Eastern and Southeastern Europe, Scandinavia, Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan.
- Skin type. Skin pigments can interfere with vitamin D synthesis, as darker skinned people produce vitamin D more slowly. eg. In just 10 minutes, a light skinned person produces 10,000 to 20,000 IU of vitamin D3. A dark skinned person may require 4 times as long or more. Darker skins, especially Black people living in the northern hemisphere, can have as little as 50% less Vitamin D than White people living in the same areas. Solar radiation for black people increases their chances of survival from cancer at a far greater percentage than white people. ie. a lack of sunshine and the related vitamin D is more devastating for darker skinned people than fair skinned people.
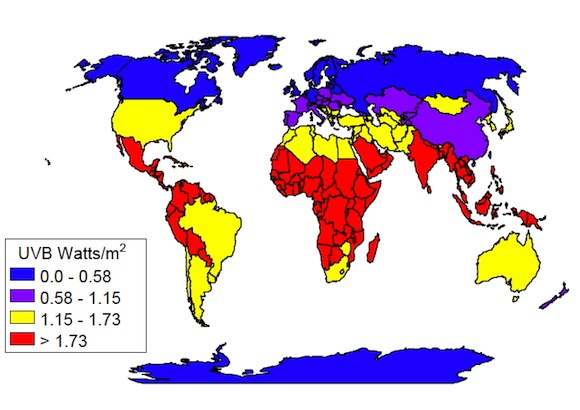
Effect of Latitude on UVB strength
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 3 - Vitamin D vs sunscreen protection
Regular sensible sunlight exposure and the resultant increase in Vitamin D levels, helps to prevent melanoma, but heavy sunlight exposure together with the use of toxic chemical sunscreens can increase your melanoma risk. This is especially so when the sunscreen offers no protection from UVA and only blocks the UVB rays, which are the very ones providing you with the ability to synthesize vitamin D. The sunscreens without UVA protection actually allow the lower layers of the skin to be damaged for longer periods of time than they would had you worn no sunscreen at all. Most of the chemical UV filter ingredients in sunscreens absorb UVB but not UVA so they do more harm than good by reducing vitamin D and increasing the risk of cancer.
A sunburn will maximise Vit D3 creation but these same benefits can be obtained without burning, so why burn? In as little as 10 minutes with full body exposure, especially if fair skinned, you may create 10,000 IU's of Vitamin D. After that you can use sunscreen, but make sure it offers both UVA and UVB protection. A physical, or otherwise known as a mineral sunscreen ingredient such as zinc oxide or titanium dioxide will offer you this broad spectrum protection.
Vitamin D fact sheet 3 summary:
- block UVA exposure to reduce melanoma risk
- maximize UVB, without burning, to maximise vitamin D
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 4 - Vitamin D and Cancer prevention
There are 20 or more internal cancers that have been identified by various scientific bodies and research, that Vitamin D3 has been seen to reduce or inhibit, including:
- kidney - Several studies indicate vit d being a strong inhibitor to kidney cancer. (1)
- leukemia - Insufficient Vitamin D Levels in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients were shown to be linked to the progression and death of these patients. (2)
- lung - people with high Vit D levels recover significantly better from lung surgery than those with low levels. (3)
- lymphoma - it appears that there is a 20 - 40 % reduced risk if exposed to sunlight and the related increase in Vitamin D. ie. A history of high UV exposure was associated with reduced risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (4)
- myeloma - or cancer of the bone marrow. The greater the level of Vitamin D, the greater the inhibitory effect. (5)
- breast - Vitamin D has been shown to block the growth of breast cancer tumors. Vitamin D's active form, calcitriol, provides numerous benefits against cancer. This form of vitamin D encourages cells to either adapt to their organ or commit apoptosis. Calcitriol also limits blood supply to the tumor and reduces the spread of cancer. (6)
- prostate - Vitamin D may prevent prostate cancer at the earliest stages as well as reduce the risk of death from prostate cancer.
- ovary - A study found that U.S. women with ovarian cancer were four times more likely to have low vitamin D blood levels than women without ovarian cancer.
- endometrial - In a U.S. study, women with endometrial cancer were four times more likely to have low vitamin D levels.
- cervical - 25(OH)D may be of significant importance for the growth control in normal and malignant cervical tissue. Normal cervical tissue and cervical cancer cells may be new targets for cancer prevention or cancer treatment with precursors of biologically active vitamin D analogues. (7)
- colorectal - Based on studies of colon and rectal cancer, vitamin D levels above 40 ng/mL (100 nmol/L) may reduce the risk of cancer. Taking 10004000 international units (IU) (25100 mcg)/day of vitamin D may lower colorectal cancer risk.
- melanoma - According to Dr Gorham M.P.H., Ph.D of the University of California, San Diego, skin cancer (melanoma) is most common where there is little sunshine and people live indoors. The most important source of vitamin D is sunlight and it inhibits the growth of melanoma by 60%. Deep penetrating UVA light is the main cause of malignant melanoma. Other studies have suggested that UVB may, paradoxically, be protective against melanoma through a mechanism involving photo-protective accommodation and photosynthesis of vitamin D in the skin.
- pancreatic - Pancreatic cancer was shown to decrease as exposure to sunlight increased.
- brain - people born to mother's with low Vit d are likely to have a increased risk of acquiring brain cancer. Vit D has been shown to cause the death of brain cancer cells taken from humans.
- bladder - Bladder cancer cell growth is inhibited by an increase in Vitamin D
- Others include esophageal, stomach, rectal, bile duct, gallbladder
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 5 - Bones, osteoporosis and arthritis
Weak bones result when calcium that regularly leaves the body through excretion, is greater than that absorbed by the bones. Vitamin D is essential for calcium to be absorbed correctly through the intestines. If our Vit D levels are good, we only need a small amount of calcium. Conversely, we can consume enormous amounts of calcium with no effect if Vitamin D levels are not high enough.
Vitamin D is also required for successful absorption of calcium into the bones.
Osteomalacia as well as fibromyalgia have been successfully treated with both Vitamin D supplementation as well as increased sunlight exposure.
Vitamin d supplementation has also been seen to halt the progress of arthritis and decrease the loss of joint cartilage.
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 6 - autoimmune diseases
Vitamin D has been shown to be crucial to the intelligent functioning of the T-cells, so with supplementation has the ability to suppress or even prevent the relevant autoimmune disease. Examples are of where immune system T-cells assault and kill certain targeted organs:
- Rheumatoid arthritis - the T cells attack the collagen producing cells of the joints
- Type-1 diabetes - the T cells attack and destroy the islet cells that produce insulin
- Multiple sclerosis - the T-cells attack the insulation surrounding the nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, called the myelin sheath, causing a sort of short circuit from the brain to the body
Sunlight and vitamin D lowers cholesterol and blood pressure. Also, the lower the level of vitamin D, the greater the risk of arterial calcification. Some other auto-immune diseases helped with Vitamin D supplementation are:
- Lupus - can attack almost any system in the body
- Inflammatory Bowel (IBS) - inflammation of the intestine with chronic diarrhea
- Crohn's disease - an inflammatory bowel disease
- Parkinsons disease - progressive disease of the nerves of the brain and spinal cord
- Cardiovascular (CVD) disease - aligns with high blood pressure and serum cholesterol higher than 150.
Vitamin D fact sheet no. 7 - Diet
An alkaline diet rich in fruit and vegetables rather than acidic animal products is also beneficial for efficient conversion of vitamin D to calcitriol, the active form of Vitamin D.
Populations with high animal protein consumption have far greater bone fractures than those with low consumption rates. Sunlight exposure has the ability to build bone mass and reduce the rate of bone fracture rates so eliminate fats not sunshine.
Increasingly, nutritionists recommend that you boost your daily intake because of Vitamin D's potential to help fight certain types of cancer. A short stroll in the sun supplies enough vitamin D to maintain healthy bones, as it is believed that vitamin D tells the body to absorb more bone-building calcium from foods.
In a study of 47,800 men, scientists at the Harvard School of Public Health reported that 1500 International Units (IU) daily of vitamin D reduced the risk of cancers of the digestive system by 43%. Another study from the University of California at San Diego, containing 1760 women, suggested that 2700 IU daily of Vitamin D may reduce breast cancer by 50%.
The most powerful source of vitamin D is the sun. In just 10 minutes, a light skinned person produces anything from 10,000 to 20,000 IU of vitamin D. Skin pigments can interfere with vitamin D synthesis, as darker skinned people produce vitamin D more slowly.
If you cannot get into the sun for various reasons, know your foods high in Vitamin D, or you can resort to pharmaceutical supplementations.
Vitamin D fact sheet referrences:
Ultraviolet radiation exposure and risk of malignant lymphomas.
Dr. Friedrich and colleagues at the University of Saarland in Germany
Association Between Altitude and Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients
Source of data used for creation of the map: Dan Lubin and associates, California Space Institute, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego
"Your Best Health Under the Sun" by Al Sears, MD And Jon Herring
"Vitamin D3 and Solar Power for optimal health" - by Marc Sorenson, EdD.
Grant W. Risk and "Risk reduction factors for colon cancer"
UVB/vitamin D and colorectal cancer essay.
 Feeling tired, foggy, or struggling with stubborn weight gain—especially around the waist? You might be surprised to learn that these symptoms could be linked to insulin resistance, a condition that a…
Feeling tired, foggy, or struggling with stubborn weight gain—especially around the waist? You might be surprised to learn that these symptoms could be linked to insulin resistance, a condition that a… Are you struggling with irregular cycles, unwanted hair growth, or unexplained fatigue? You’re not alone. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age—and many mor…
Are you struggling with irregular cycles, unwanted hair growth, or unexplained fatigue? You’re not alone. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age—and many mor… While progesterone is often discussed in relation to reproductive health, emerging research reveals its remarkable role in supporting brain function and protecting against neurological decline. Proges…
While progesterone is often discussed in relation to reproductive health, emerging research reveals its remarkable role in supporting brain function and protecting against neurological decline. Proges… Incase you missed it!
Today is the last day for you to claim 15% off our Natpro 100ml Dispensers. The sale ends at midnight tonight.
How to Claim Your 15% Discount:
•Shop at
Incase you missed it!
Today is the last day for you to claim 15% off our Natpro 100ml Dispensers. The sale ends at midnight tonight.
How to Claim Your 15% Discount:
•Shop at